Horta da Terra Ltda
This page summarizes the Horta design details for the implementation of the environmental monitoring and evaluation indicator requirements by the Amazon Biodiversity Fund (ABF).
2021 Horta Report (pdf) 2022 Horta Report (pdf)
Location
Horta da Terra Ltda (hereafter Horta da Terra) is one of ABF’s first signed business deals classified under investment pillar 3-Sustainable Farming. Horta da Terra’s office and processing plant are located in Belém, Para, but its production farm is located northeast about 1.5 hours from Belém and close to Santo Antonio de Taua (Fig. 1). The young business startup began in 2019 with the goal of commercializing Non-Conventional Food Plants (PANCs in Portuguese) native to the Amazon. Through organic and Syntropic production methods, Horta da Terra uses sustainable production systems and freeze-dried technologies to promote human health and agrobiodiversity conservation.
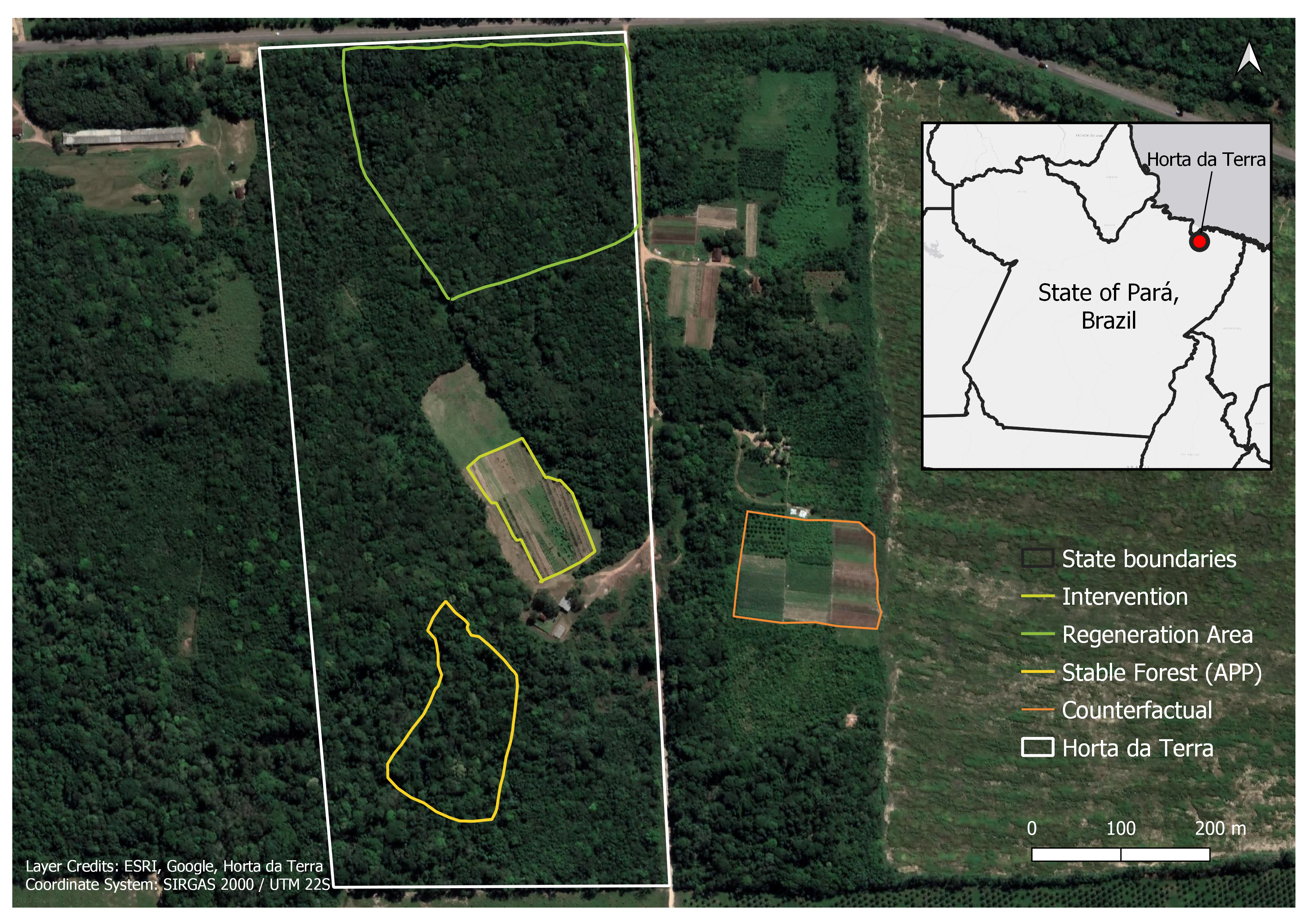
Land Uses / Geographic Reporting Units
The application of TerraBio’s at Horta da Terra was co-design to monitor four distinct land cover/Land use types: (i) Forest Reference area, (ii) Forest Enrichment of Restoration site, (iii), Syntropic system, (iv) conventional agricultural plot as a Counterfactual. The Forest Enrichment and the Syntropic system are intervention activities carried out by Horta to be monitored by TerraBio. The Forest Reference area serves as a natural environment, and the Counterfactual plot serves as a business-as-usual non-sustainable agricultural activity, both areas to compare Horta’s results with.
The land uses we include in the design of TerraBio include:
- Reference: Conserved forested area characterized by native trees.
- Counterfactual: Practice followed if no intervention. E.g. pasture land, soy plantation.
- Intervention Type(s): 3.1 Syntropic system 3.2 Forest Enrichment
- Undesignated: Note, not all areas in a farm will fall under these categories. We refer to this area in the farm that is not included as an intervention, reference or counterfactual as undesignated.
Farm boundary(ies): Includes the farm boundaries under the deal. It usually encompasses all the other land uses, but it can happen that one land use is not within the farm boundaries.
Intervention Details (SAF)
A current total of 3 hectares have been assigned for the implementation of a Syntropic system, of which as of 2022 only 2 hectares encompass the Syntropic plot and 1 hectare is pasture. Syntropic agriculture is also defined as successional agroforestry, where the productive system attempts to replicate ecosystem processes and principles (Andrade et al. 2020). At Horta da Terra the Syntropic system was implemented between 2020 and 2021. The multistrata production system is composed by a total of 4 layers. A ground layer is made up by species such as jambu, chicoria, cariru, and espinafre A lower-mid layer is composed of taioba, batata aria, camapu, cubiu. A mid layer contains species such as vinagreira roxa e verde, ora-pronobis, cipo alho, graviola, gliricidia, and banana. Last, a canopy layer is composed of parica, jaca, guapuruvu, sinomomo, and moringa. The canopy layer has a current height of 3 meters.
Forest Enrichment Details (Restoration)
An area of about 7.5 hectares is being restored by planting high economical and ecological value species such as Andirona, Ipe, Parica, Copaiba, Jatoba. The planting of 58 Andiroba seedling was done in a single line every 5 meters. Existing dominant tree species in the forest enrichment area include Ingá de corda, Ingá vermelha, Sapucaia, Cedro, Imbaúba, Araça da mata, Tachi, Cupiuba, and their average height is about 7 meters.
Forest Reference Details
The Forest Reference area at Horta da Terra is part of a Permanent Protected Area (APP as per its acronym in Portuguese. An APP is a natural vegetation patch according to Brazil’s Forest Code). The sampled area is about 2.1 hectares of mature secondary growth forest. The area has a close canopy with trees about 10 meters in height. Some of the species present in this area include Cupiuba,Virola, Inga Vermelh, Mogno, Louro, Tapiririca, Cumaru, Cedro, Guaruba, and Sapucaia. The area was last cleared around 15 years ago. As a characteristic of the sampled area, it contains a natural water source, which is way it should be considered an APP.
Counterfactual Pasture Details (Pasture)
The traditional agricultural plots of Horta’s neighbor were identified as a Counterfactual to compare results. The neighbor produces various products in a more conventional manner. Some of the main crops include papaya production, lettuce, cilantro, green peppers, green cabbage, chive, gherkin, jambu, and chicoria. Additional products not planted in 2022 include passion fruit. Some of the products are interplanted and the farmer practices crop rotation in his plots. Conventional practices include the use of machinery for tilling, and synthetic fertilizers (e.g., NPKs) as well as the use of pesticides (herbicides, insecticides, and fungicides). In addition, the farmer uses burning practices sometimes to clean fields from remaining plant residues.
Remote Sensing Indicators Quick Look Up Table
| ABF KPI | TerraBio metric | reporting unit | measurement units |
|---|---|---|---|
| CO2 e Reduction | Carbon Sequestration - Emission Reductions | farm boundary and by land use | normalized by area (T C/ha - confirm units) |
| Improved Biophysical Conditions | Regenerated/Restored Area | within intervention sites | Total ha |
| Landscape Conservation | Conserved Forest Area | farm boundary, excluding intervention | Total ha |
| Habitat Protection | Change in Patch Connectivity | farm boundary | percent area change per class |
Sample Design
Sample Design for Image Interpretation
Sample points were generated following the following steps:
- simple random sample of 80 points within the farm boundary
- 8 additional random points from pixels classified as deforestation or degradation to meet data needs
- 10 more random points only within the counterfactual site, used only for carbon sequestration-emission reduction metric calculation
Visit resources below for more details:
- Notes on Horta Year 1 (2021) Sample Design
- GEE script for initial simple random sample
- GEE script for additional points
LandTrendr Loss Parameterization
Table 1. LandTrendr collection parameters and filters.
| Parameter | Description | Values (Horta 2022) | Values being tested |
|---|---|---|---|
| Spectral index | Input variable to be segmented | NBR | |
| delta | Loss or Gain | loss | |
| sort | Type (greatest, least, newest, oldest, fastest, or slowest) | greatest | |
| startYear | Start year of image collection | 2017 | 1985 |
| endYear | End year of image collection | 2021 | 2022 (for 2023) |
| startDay | The minimum date in the desired seasonal range over which to generate annual composite (MM-DD) | 06-20 | |
| endDay | The maximum date in the desired seasonal range over which to generate annual composite (MM-DD) | 09-20 | |
| year filter | Filter by specific period of time (true or false) | false | true |
| year filter start | Filter start year | remains the same as startYear | 2021 |
| year filter end | Filter end year | remains the same as endYear | 2022 |
| magnitude | Magnitude filter (true/false) | true | |
| magnitude value | Magnitude value | 100 | 50, 200 |
| magnitude operator | Less than or greater than | > | > |
| duration | Duration filter (true/false) | false | |
| duration value | Duration value in years | N/A | 50 |
| duration operator | Less than or greater than | N/A | < |
| preval | Pre-change spectral value filter (true/false) | false | |
| preval value | Pre-change spectral value | N/A | 300, 400, 500 |
| preval operator | Less than or greater than | N/A | > |
| mmu | Minimum mapping unit | false | |
| mmu value | MMU value in pixels | N/A | 6 |
Table 2. LandTrendr run parameters and values. These were based off of previous studies and can be used to start testing as we transfer the mapping algorithm to new locations (Kennedy et al., 2018, Kennedy et al 2010).
| Parameter | Description | Values tested | Horta (2022) |
|---|---|---|---|
| despike | Before fitting, spikes are dampened if the spectral value difference between spectral values on either side of the spike is less than 1-despike desawtooth proportion of the spike itself. Lower values filter spikes more aggressive Nc setting to 1.0 turns off. | 0.75, 0.9, 1 | 0.9 |
| pval | If best fitted trajectory’s p-of-F value exceeds this threshold, the entire trajectory is considered no-change. | 0.05, 0.1, 0.2 | 0.1 |
| max segments | The maximum number of segments allowed in fitting | 4, 5, 6 | 5 |
| prevent one year recovery | Prevent segments that represent one year recoveries | false | false |
| recovery threshold | During fitting, if a candidate segment has a recovery rate faster than 1/recovery_threshold (in years), that segment is disallowed and a threshold different segmentation must be used. Setting to 1.0 turns off this filter. | 0.25, 0.5, 1 | 0.5 |
| vertex count overshoot | The initial regression-based detection of potential vertices can overshoot (max_segments+ 1) vertices by this value; angle-based culling is used to return to the desired number of vertices if overshoot occurs. Allows a mix of criteria for vertex identification. | 3 | 3 |
| min observations needed | Minimum observations needed to perform output fitting | 6 | 6 |
| best model proportion | Takes the model with most vertices that has a p-value that is at most this proportion away from the model with lowest p-value | 0.75 | 0.75 |
LandTrendr Gain Parameterization
Table 1. LandTrendr collection parameters and filters.
| Parameter | Description | Values (Horta 2022) | Values being tested |
|---|---|---|---|
| Spectral index | Input variable to be segmented | NBR | |
| delta | Loss or Gain | gain | |
| sort | Type (greatest, least, newest, oldest, fastest, or slowest) | greatest | |
| startYear | Start year of image collection | 2017 | 1985 |
| endYear | End year of image collection | 2021 | 2022 (for 2023) |
| startDay | The minimum date in the desired seasonal range over which to generate annual composite (MM-DD) | 06-20 | |
| endDay | The maximum date in the desired seasonal range over which to generate annual composite (MM-DD) | 09-20 | |
| year filter | Filter by specific period of time (true or false) | false | true |
| year filter start | Filter start year | remains the same as startYear | 2021 |
| year filter end | Filter end year | remains the same as endYear | 2022 |
| magnitude | Magnitude filter (true/false) | true | |
| magnitude value | Magnitude value | 100 | |
| magnitude operator | Less than or greater than | > | |
| duration | Duration filter (true/false) | false | |
| duration value | Duration value in years | N/A | |
| duration operator | Less than or greater than | N/A | |
| preval | Pre-change spectral value filter (true/false) | false | |
| preval value | Pre-change spectral value | N/A | |
| preval operator | Less than or greater than | N/A | |
| mmu | Minimum mapping unit | false | |
| mmu value | MMU value in pixels | N/A |
Table 2. LandTrendr run parameters and values (Kennedy et al., 2018, Kennedy et al 2010).
| Parameter | Description | Horta (2022) |
|---|---|---|
| despike | Before fitting, spikes are dampened if the spectral value difference between spectral values on either side of the spike is less than 1-despike desawtooth proportion of the spike itself. Lower values filter spikes more aggressive Nc setting to 1.0 turns off. | 0.9 |
| pval | If best fitted trajectory’s p-of-F value exceeds this threshold, the entire trajectory is considered no-change. | 0.1 |
| max segments | The maximum number of segments allowed in fitting | 5 |
| prevent one year recovery | Prevent segments that represent one year recoveries | false |
| recovery threshold | During fitting, if a candidate segment has a recovery rate faster than 1/recovery_threshold (in years), that segment is disallowed and a threshold different segmentation must be used. Setting to 1.0 turns off this filter. | 0.5 |
| vertex count overshoot | The initial regression-based detection of potential vertices can overshoot (max_segments+ 1) vertices by this value; angle-based culling is used to return to the desired number of vertices if overshoot occurs. Allows a mix of criteria for vertex identification. | 3 |
| min observations needed | Minimum observations needed to perform output fitting | 6 |
| best model proportion | Takes the model with most vertices that has a p-value that is at most this proportion away from the model with lowest p-value | 0.75 |
Spectral indices
- For mapping loss and degradation we used: NBR
- For mapping regrowth we used: NBR
- For mapping stand age: NBR